Not many people know what Tissue Culture essentially means, so let’s start from the basics here. In the very vast developing scenario, the plant tissue culture has taken lead as the most promising areas of application of the biotechnological tools for today’s and tomorrow’s agricultural scenario. Plant production can be carried out throughout the year irrespective of the season or weather conditions. Tissue Culture means cloning and micro-propagating the tissues of selected plants. It is the growth of cells in an artificial medium, separate from the organism. It is the modern technology that can be applied for mass production of superior grade planting material for most crops. However, micropropagation technology is an expensive venture, as compared to the other existing conventional methods. Therefore, extreme care must be taken and it is essential to adopt measures to reduce the cost of production. As such, Plant Tissue Culture has a great role to play in agricultural development and productivity.
The tissue culture process mainly consists of five important steps: Initiation, multiplication, shooting and rooting, primary hardening in greenhouses and lastly, secondary hardening in shade houses. To be successful in plantation via tissue culture method, one should take care of the micro-climatic conditions and adhere to hygiene standards during the hardening process. Tissue culture is the right approach that can solve these problems.
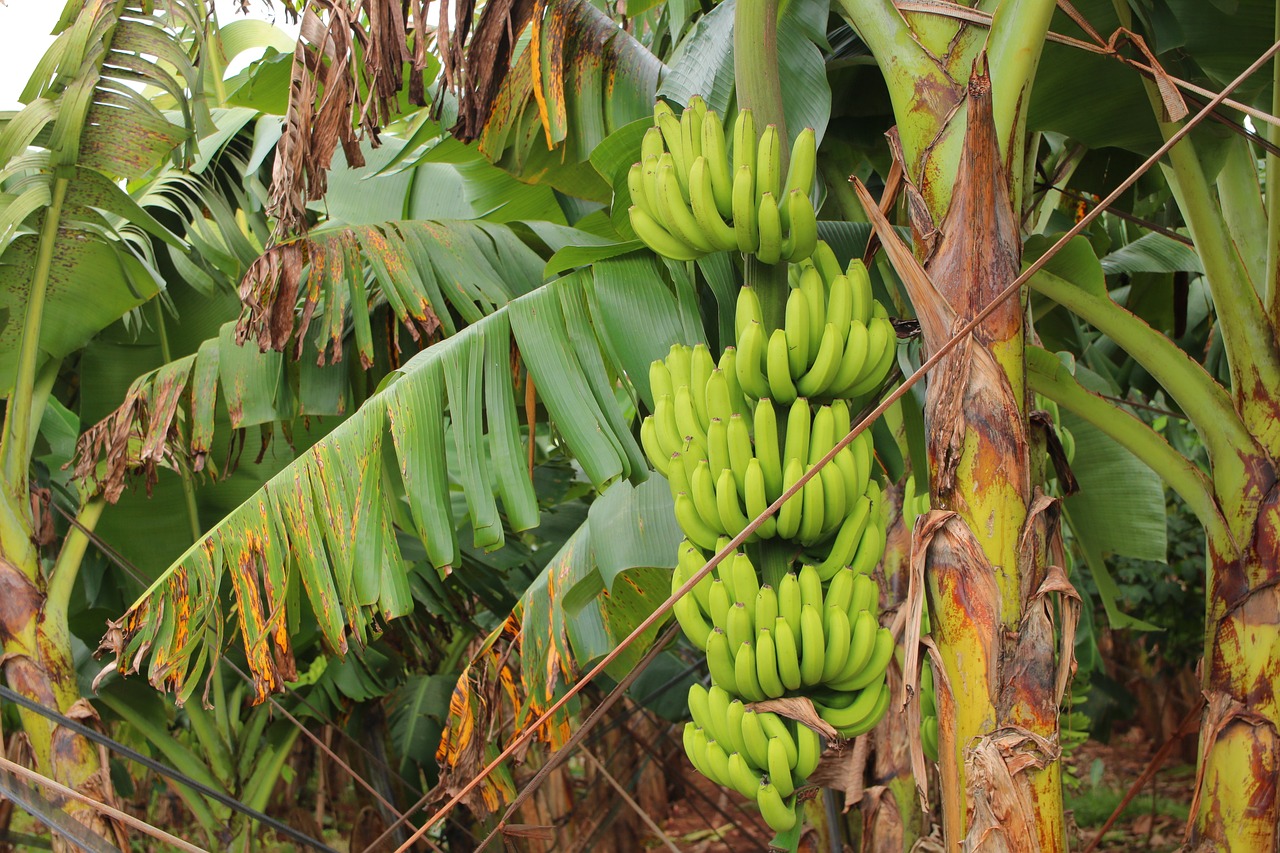
During the clonal selection process, healthy, high yielding and quality donor banana plants are screened and identified. As part of the initial phase of tissue culture, the Meristem tissue portion of the bud is taken out of the basil corm of the donor banana plants, inoculated to an artificial nutrient media. The initial tissue will be disease-free, due to rapid cell division, and in a controlled environment at the lab which can be multiplied into numerous folds to obtain the required number of each banana variety. Subsequently, the Banana Tissue Culture Plants are released from the lab to a climate-controlled environment. This requires about 3 to 4 weeks to complete the primary hardening process. Secondary hardening of plants can be pursued in secondary controlled environments. Also, it is important to grade the plants based on their height and girth before planting in the main field. After about 8 to 10 weeks of the secondary nursery process, they should be transplanted to the main field. The schedule and kind of fertilizers in tissue culture plantation depends on soil fertility. It is imperative to protect the plants from dislodging due to strong winds or heavy fruit bearings. This can be effectively done by propping with bunches with sticks.
The cost of Tissue Cultured Banana Plants may vary depending on age and variety. Usually, the price may vary from Rs 10 to 25 Rs. Depending upon the variety. Bananas can be grown year-round without any shortage of tissue cultured plant materials if the selected area has a proper irrigation facility. The advantage of the banana tissue cultured process is that banana plants produce uniform maturity/growth of fruits which can make the task of harvesting easy and result in low labor cost.
To sum up, bananas produced from ‘banana tissue culture plants’ fetch a better price in the market due to their quality and uniformity. Bananas are the favorite fruit in our grocery basket and are grown by millions of farmers and plantation workers. Bananas are the staple food for millions of people in developing countries, and banana trade is a cornerstone of many of these developing countries’ economies.






 WhatsApp us
WhatsApp us